
Introduction: Where Nature Meets Innovation
In the evolving landscape of eco-conscious design, bio-based materials have become the perfect fusion of science and sustainability. Derived from renewable resources, they’re transforming not only what fashion is made from but also how it’s made.
According to Fashion Audit, 2025 is the defining year when bio-based materials move from niche experiments to mainstream production, appearing in everything from sneakers and handbags to couture garments. Consequently, the line between natural and technological design is fading faster than ever.
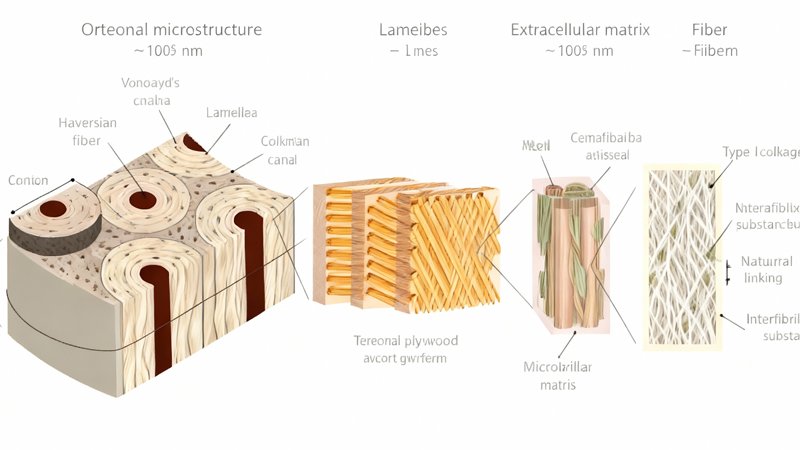
1. What Are Bio-based Materials?
Bio-based materials come from renewable biological sources such as plants, fungi, algae, or agricultural by-products. Unlike synthetic materials that rely on petroleum, they draw energy and structure from nature itself.
As a result, they offer designers a cleaner, greener way to produce durable, fashionable, and biodegradable products.
Fashion Audit Insight: Bio-based materials are not simply replacements — they’re the blueprint for fashion’s next sustainable era.
2. The Science Behind Bio-based Innovation
Bio-based materials are developed through biopolymer technology, a process that converts natural substances — like cellulose, starch, or oils — into usable fibers, resins, and textiles.
In simpler terms, it means turning plant molecules into materials that can replace plastic, leather, or polyester. Furthermore, biotechnology allows customization, enabling materials to have the same flexibility or durability as their synthetic counterparts.
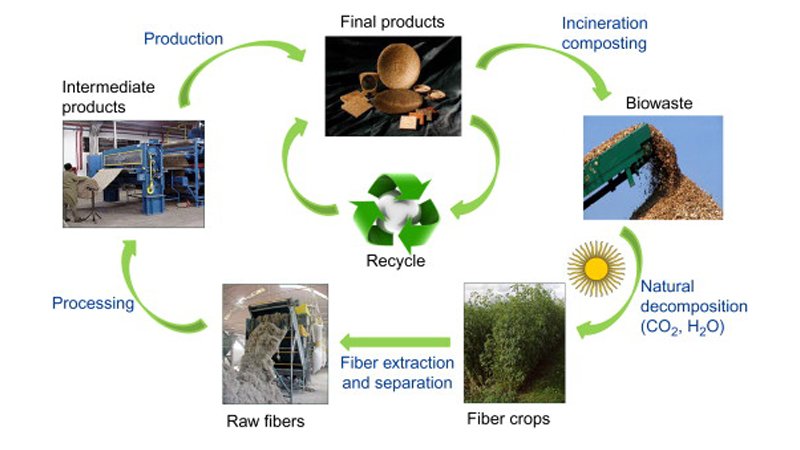
3. Why Bio-based Materials Matter
The global fashion industry consumes enormous natural resources each year. However, by embracing bio-based alternatives, it can significantly reduce pollution, emissions, and waste.
Key Benefits:
- They are renewable and biodegradable, meaning less landfill waste.
- Production creates a lower carbon footprint compared to fossil-derived materials.
- They are non-toxic and safer for both makers and wearers.
- They support regenerative agriculture, improving soil health.
Fashion Audit Note: Bio-based innovation doesn’t just sustain—it regenerates. It gives back to the environment rather than taking from it.
4. Types of Bio-based Materials in Fashion
The fashion industry is witnessing a rapid rise in several bio-material innovations. Each type serves a unique purpose and caters to different fashion needs.
4.1 Bio-based Leather Alternatives
Materials such as Piñatex (pineapple leaves), Mylo™ (mushrooms), and Desserto® (cactus) have revolutionized the concept of leather.
Benefits: They are renewable, biodegradable, and cruelty-free.
4.2 Bio-based Textiles
Fibers like orange fiber, hemp, and bacterial cellulose are replacing synthetic fabrics. They are soft, breathable, and naturally biodegradable.
4.3 Bio-based Plastics (Bioplastics)
Derived from starches or sugarcane, these are used in shoe soles, packaging, and buttons. In contrast to petroleum-based plastics, they decompose naturally over time.
4.4 Bio-based Foams
Plant-derived EVA or algae-based foams are reshaping footwear comfort. Moreover, they provide exceptional cushioning without harming the planet.
4.5 Bio-based Dyes
Pigments from roots, plants, and fruits are replacing harsh chemicals. Therefore, bio-based dyes make fashion cleaner and safer for workers and ecosystems alike.
Fashion Audit Observation: Every bio-based innovation tells a story of responsibility — connecting craftsmanship with the rhythm of nature.
5. How Bio-based Materials Are Made
The production of bio-materials is a blend of biology, chemistry, and engineering.
- Sourcing: Plants, algae, and organic waste are collected.
- Processing: Biomass is broken down into natural polymers.
- Conversion: Polymers are reformed into fibers, films, or foams.
- Manufacturing: These are used to craft textiles, soles, or accessories.
Consequently, fashion items made with bio-based materials leave a much lighter footprint on the planet.
6. Bio-based Materials in Footwear
Bio-based technology has become a key player in footwear innovation. From soles to linings, every part of the shoe can now be plant-derived.
| Component | Bio-based Alternative | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Uppers | Hemp, Piñatex, or cork | Breathable and durable |
| Midsoles | Sugarcane EVA or algae foam | Lightweight cushioning |
| Outsoles | Natural rubber | Excellent traction |
| Linings | Organic cotton or cork | Moisture control |
| Adhesives | Bio-resins | Non-toxic bonding |
Fashion Audit Tip: A truly sustainable shoe starts with nature at every layer — from the sole to the stitch.
7. Bio-based vs Synthetic Materials
| Aspect | Bio-based Materials | Synthetic Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable (plant or microbial) | Fossil fuels |
| Eco Impact | Low carbon footprint | High emissions |
| Durability | High with innovation | High |
| Biodegradability | Yes | No |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic | Often chemical-based |
| Cost | Slightly higher | Lower initially |
Although bio-based materials may cost more at first, their benefits far outweigh their price. In the long term, they promote environmental health and material longevity.
Fashion Audit Verdict: Bio-based materials are not only sustainable—they’re smart investments in the future of fashion.
8. Examples of Leading Bio-based Innovations (2025)
| Material | Source | Used In |
|---|---|---|
| Piñatex | Pineapple leaves | Vegan leather |
| Mylo™ | Mushroom mycelium | Bags and jackets |
| BLOOM Foam | Algae biomass | Shoe midsoles |
| Bio-EVA | Sugarcane | Footwear and packaging |
| QMilk | Milk protein waste | Textiles |
| Orange Fiber | Citrus by-products | Apparel fabrics |
Furthermore, these materials are becoming commercial staples across both luxury and mainstream markets.
9. Environmental Impact and Benefits
The ecological advantages of bio-based materials extend beyond carbon savings:
- They reduce waste by repurposing agricultural by-products.
- They use less water compared to conventional textiles.
- Their production requires less energy overall.
- Most importantly, they biodegrade naturally, closing the loop of production.
Fashion Audit Observation: Bio-based fashion is circular by nature — it begins with the earth and eventually returns to it.
10. Challenges and Future Solutions
While bio-based materials are promising, the transition isn’t without obstacles.
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| High production costs | Automation and scale manufacturing |
| Supply chain limits | Diversified sourcing from multiple crops |
| Early durability issues | Hybrid blends with natural fibers |
| Consumer awareness | Transparent education and labeling |
Therefore, collaboration between scientists, designers, and policymakers is crucial for mass adoption.
11. Leading Brands Using Bio-based Materials
| Brand | Innovation | Material Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Adidas | Futurecraft Loop | Bio-based TPU and algae foam |
| Stella McCartney | Mylo™ mushroom leather | Luxury sustainability |
| Allbirds | SweetFoam™ | Sugarcane EVA |
| Veja | Bio-rubber and rice waste | Ethical sneakers |
| Pangaia | Seaweed fiber and bio-nylon | Eco-activewear |
Fashion Audit Note: These brands show that sustainability and luxury can coexist beautifully when powered by innovation.
12. The Future of Bio-based Materials in Fashion
As innovation accelerates, the possibilities are endless.
Emerging trends include:
- 3D-printed bio fabrics for custom garments.
- Fully compostable textiles that vanish naturally.
- AI-optimized recycling systems.
- Hybrid bio-leathers for durability and texture.
As Fashion Audit highlights, this is not just a material evolution — it’s a mindset revolution.

FAQs About Bio-based Materials
1. Are bio-based materials biodegradable?
Yes, most are naturally biodegradable or compostable under industrial conditions.
2. How durable are they?
Newer bio-composites like Mylo and sugarcane EVA are both flexible and long-lasting.
3. Are they expensive?
Currently, they cost slightly more, but prices are dropping as technology improves.
4. Can they replace plastics completely?
In many industries — especially fashion — yes, they already do.
5. Does Fashion Audit recommend bio-based materials?
Absolutely. Fashion Audit champions bio-based innovation as the foundation of sustainable design.
Conclusion: From Growth to Greatness
In the journey toward sustainable fashion, bio-based materials stand as proof that innovation and nature can coexist harmoniously. They offer comfort, quality, and conscience in equal measure — transforming not just products, but principles.
As Fashion Audit beautifully summarizes:
“The future of fashion isn’t man-made — it’s nature-made.”
Disclaimer:
All trademarks, logos, product names, and brand identifiers mentioned on FashionAudit.com are the property of their respective owners. They are used solely for the purpose of product review, comparison, and consumer information. FashionAudit.com does not claim any ownership of these marks.
No copyright or trademark infringement is intended. If any brand or rights holder believes their intellectual property has been misused, they can contact us directly and we will address the issue promptly.